You are here: Foswiki>Cosmo Web>MediaShapeUniverse>CosmoGroupRollUp2023 (07 Sep 2023, BoudRoukema)Edit Attach
<< Cosmo
Content for poster (roll-up/pull-up banner) to be printed by UMK public relations department
Tekst w kursywie jest tylko wyjaśnienia, to nie treść dla pull-up banner; obrazy są pod CC BY lub CC0, jak napisano.- keywords:
- Kosmologia - Cosmology
- Topologia kosmiczna - Cosmic topology
- Kosmologia niejednorodna - Inhomogeneous cosmology
- key questions:
- Jaki jest kształt Wszechświata? - What is the shape of the Universe?
- Czy Wszechświat jest skończony ale nieograniczony ? - Is the Universe finite without edges?
- Czy ciemna energia to tylko pustki kosmiczne? - Is dark energy just cosmic voids?
- Images:
-
-
 (C) 2022 ESA/Webb CC BY 4.0
(C) 2022 ESA/Webb CC BY 4.0 - no text needed except for (C) 2022 ESA/Webb CC BY 4.0
-
-
-
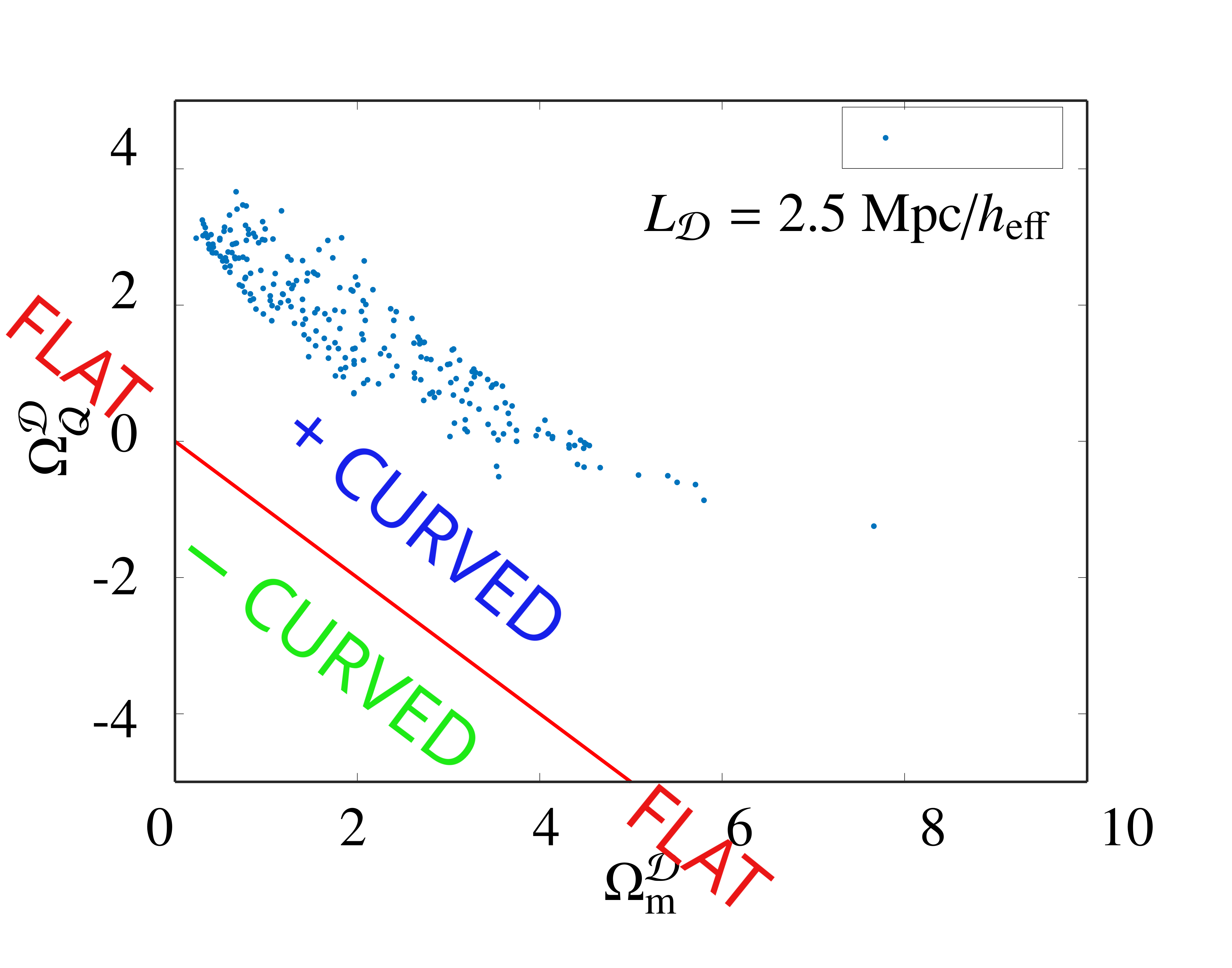 (C) 2023 B. Roukema CC BY 4.0
(C) 2023 B. Roukema CC BY 4.0 - text: Galaxies and their dark matter haloes form from small density perturbations in the expanding Universe. These overdense regions expand more slowly than the rest of the Universe and eventually "turn around" – start collapsing instead of expanding. The blue dots in this figure (for a standard ΛCDM reference model) show that at this turnaround epoch, these galaxy formation regions are positively curved. If the Universe were flat, galaxies could not be formed. Roukema & Ostrowski 2019, JCAP 12, 049 [arXiv:1902.09064],
https://codeberg.org/boud/1902.09064
- text: Galaxies and their dark matter haloes form from small density perturbations in the expanding Universe. These overdense regions expand more slowly than the rest of the Universe and eventually "turn around" – start collapsing instead of expanding. The blue dots in this figure (for a standard ΛCDM reference model) show that at this turnaround epoch, these galaxy formation regions are positively curved. If the Universe were flat, galaxies could not be formed. Roukema & Ostrowski 2019, JCAP 12, 049 [arXiv:1902.09064],
-
-
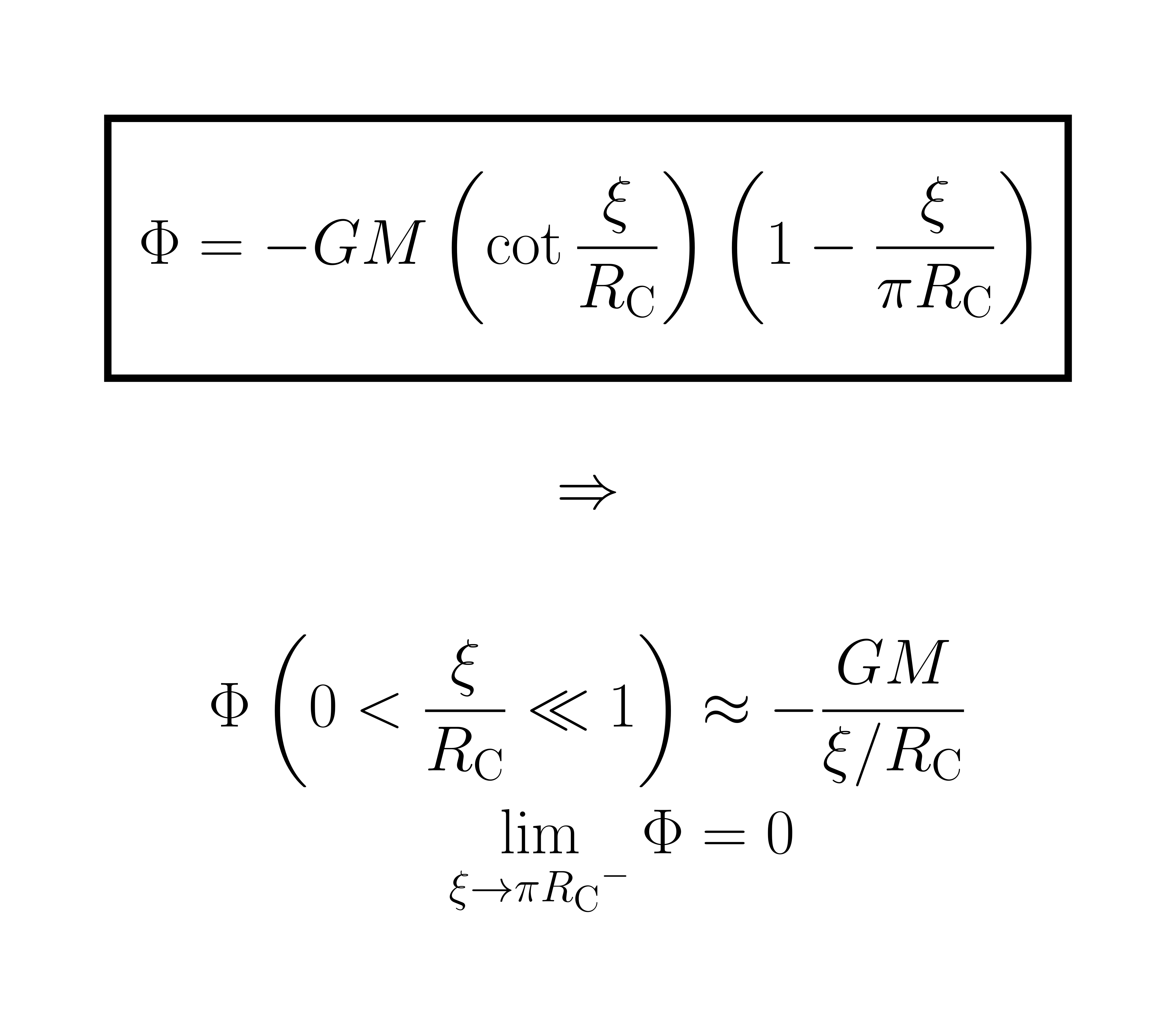
(C)2023 B. Roukema CC0- text: How can Newtonian gravitation, our non-relativistic theory of gravitation, be extended to non-Euclidean topologies? That question was answered by Vigneron (2022, CQG, 39, 155006), using a mathematical object known as Galilean structure. This "non-Euclidean Newtonian theory of gravitation" predicts, in particular, how the topology of the Universe influences the gravitational potential created by a massive object. If the space of our Universe has hyperspherical curvature, then Newton's law written as a potential, i.e. −GM/r, is not valid and must be replaced by the formula above at a distance ξ, where RC is the hyperspherical radius (and a closed straight circle has length 2πRC). While the observational effect of the difference with Newton's law is likely to be tiny, this formula shows that the topology of the Universe, can, in principle, be measured, no matter how big the Universe is. Vigneron & Roukema 2022, PRD 107, 063545 [arXiv:2201.09102],
https://codeberg.org/boud/topoaccel
- text: How can Newtonian gravitation, our non-relativistic theory of gravitation, be extended to non-Euclidean topologies? That question was answered by Vigneron (2022, CQG, 39, 155006), using a mathematical object known as Galilean structure. This "non-Euclidean Newtonian theory of gravitation" predicts, in particular, how the topology of the Universe influences the gravitational potential created by a massive object. If the space of our Universe has hyperspherical curvature, then Newton's law written as a potential, i.e. −GM/r, is not valid and must be replaced by the formula above at a distance ξ, where RC is the hyperspherical radius (and a closed straight circle has length 2πRC). While the observational effect of the difference with Newton's law is likely to be tiny, this formula shows that the topology of the Universe, can, in principle, be measured, no matter how big the Universe is. Vigneron & Roukema 2022, PRD 107, 063545 [arXiv:2201.09102],
What is a "roll-up banner"?
LaTeX source for an example pull-up banner
This is just an example, without the UMK logo and colours.
\documentclass[portrait]{sciposter}
\renewcommand{\papertype}{custom}
\renewcommand{\fontpointsize}{25pt}
\renewcommand{\paperwidth}{800mm}
\renewcommand{\paperheight}{2000mm}
\renewcommand{\setpspagesize}{
\ifthenelse{\equal{\orientation}{portrait}}
\special{papersize=800mm,2000mm}
}{\special{papersize=2000mm,800mm}
}
%hacks
\setlength{\textheight}{1990mm}
\setlength{\textwidth}{770mm}
\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-35mm}
%\usepackage{fontspec} % xelatex|lualatex
\usepackage{fix-cm}
\usepackage{multicol}
\usepackage{graphicx}
\usepackage{hyperref}
\usepackage{suffix}
\usepackage{setspace}
\usepackage{textpos}
\usepackage[polish]{babel}
\usepackage[LGR,T1]{fontenc}
%\usepackage[T2A]{fontenc}
\usepackage[utf8]{inputenc}
\usepackage{polski}
%\usepackage{url}
\usepackage{lmodern}
%\newfontfamily\mydejavu{DejaVu Sans}
\newcommand\mytitlesize{\fontsize{70mm}{6mm}\selectfont}
\newcommand\keyquestionsone{\fontsize{35mm}{3mm}\selectfont}
\newcommand\keyquestionstwo{\fontsize{25mm}{3mm}\selectfont}
\newcommand\legendone{\fontsize{20mm}{30mm}\selectfont}
\newcommand\legendoneref{\fontsize{15mm}{2mm}\selectfont \it}
\newcommand\legendtwo{\fontsize{20mm}{3mm}\selectfont}
\newcommand\legendtworef{\fontsize{15mm}{2mm}\selectfont \it}
\newcommand\myvspace{\rule{0ex}{2ex}}
\begin{document}
{\centering
\mytitlesize Kosmologia
\myvspace
}
%\maketitle
\begin{figure}
\centering
\includegraphics[width=\textwidth]{Webb}
{\normalsize (C) 2022 ESA/Webb CC BY 4.0}
\end{figure}
\myvspace
{\centering
\keyquestionsone
Jaki jest kształt Wszechświata?
{\it What is the shape of the Universe?}
\myvspace
Czy Wszechświat jest skończony ale nieograniczony ?
{\it Is the Universe finite without edges?}
\myvspace
Czy ciemna energia to tylko pustki kosmiczne?
{\it Is dark energy just cosmic voids?}
\myvspace
}
\begin{multicols}{2}
\begin{figure}
{\centering
{\keyquestionstwo
Kosmologia niejednorodna}
\includegraphics[width=0.88\textwidth]{RO19_rerun_Fig6a}
{\keyquestionstwo \it Inhomogeneous cosmology}
\myvspace
\myvspace
}
{\legendone
Galaxies and their dark matter haloes form from small density perturbations in the expanding Universe. These overdense regions expand more slowly than the rest of the Universe and eventually ``turn around'' -- start collapsing instead of expanding. The blue dots in this figure (for a standard $\Lambda$CDM reference model) show that at this turnaround epoch, these galaxy formation regions are positively curved. If the Universe were flat, galaxies could not be formed.}
{\legendoneref
Roukema \& Ostrowski 2019, JCAP 12, 049 [arXiv:1902.09064], https://codeberg.org/boud/1902.09064}
\end{figure}
\begin{figure}
{\centering
{\keyquestionstwo
Topologia kosmiczna}
\includegraphics[width=0.88\textwidth]{NEN}
{\keyquestionstwo
\it Cosmic topology}
\myvspace
\myvspace
}
{\legendtwo
How can Newtonian gravitation, our non-relativistic theory of gravitation, be extended to non-Euclidean topologies? That question was answered by Vigneron (2022, CQG, 39, 155006), using a mathematical object known as Galilean structure. This ``non-Euclidean Newtonian theory of gravitation'' predicts, in particular, how the topology of the Universe influences the gravitational potential created by a massive object. If the space of our Universe has hyperspherical curvature, then Newton's law written as a potential, $-GM/r$, is not valid and must be replaced by the formula above at a distance $\xi$, where $R_\mathrm{C}$ is the hyperspherical radius (and a closed straight circle has length 2$\mathrm{\pi}R_{\mathrm{C}}$). While the observational effect of the difference with Newton's law is likely to be tiny, this formula shows that the topology of the Universe, can, in principle, be measured, no matter how big the Universe is.}
{\legendtworef
Vigneron \& Roukema 2022, PRD 107, 063545 [arXiv:2201.09102], https://codeberg.org/boud/topoaccel}
\end{figure}
\end{multicols}
{\centering
\myvspace
\myvspace
\mytitlesize Cosmology
\keyquestionsone [$+$ logo UMK, ,,Instytut Astronomii'', \ldots]
}
\end{document}
-- BoudRoukema - 08 Aug 2023 + ... Edit | Attach | Print version | History: r7 < r6 < r5 < r4 | Backlinks | View wiki text | More topic actions
Topic revision: r7 - 07 Sep 2023, BoudRoukema
 Copyright © by the contributing authors. All material on this collaboration platform is the property of the contributing authors.
Copyright © by the contributing authors. All material on this collaboration platform is the property of the contributing authors. Ideas, requests, problems regarding Foswiki? Send feedback
